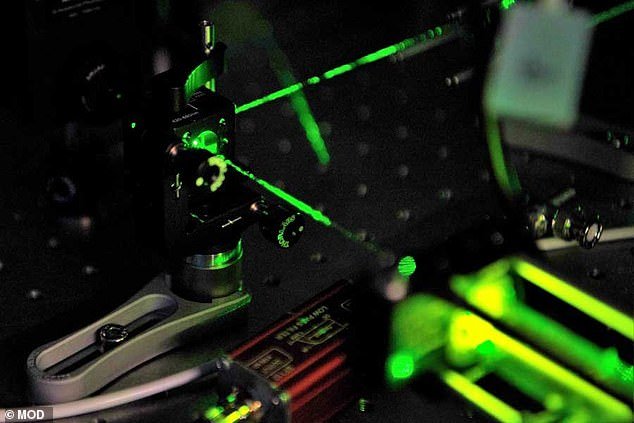
A highly classified research facility is in the process of creating an exceptionally accurate “quantum clock” that could significantly impact British intelligence.
planes.
It will also ‘enhance the accuracy of advanced weapons’ such as guided missiles and give British computer experts the upper hand over online adversaries like cyber criminals.
The clock’s precision will be so finely tuned that it will lose less than one second over millions of years, enabling scientists to measure time at an entirely new scale.
It is the first device of its kind to be constructed in the UK and will be deployable on military missions within the next five years, according to the Defence Science and Technology Laboratory (DSTL).
“This initial test of the advanced atomic clock marks a substantial milestone in the UK’s quantum technology capabilities,” said DSTL chief executive Paul Hollinshead.
‘The data gathered will not only shape future defense efforts, but it will also signal to industry and academia our serious commitment to exploring quantum technologies, with the goal of achieving secure and resilient operational advantages.’
Particle-based clocks utilize quantum physics principles to maintain time with exceptional accuracy by measuring energy variations within atomic particles.

Precision quantum clocks surpass even the accuracy of atomic clocks, of which approximately 400 are currently in service globally.
The United Kingdom presently possesses an atomic clock at the National Physical Laboratory in London, but this new quantum clock will be the first of its kind in the country.
Nick France, CTO of Sectigo, stated to MailOnline, “A quantum clock is a type of atomic clock – basically a highly precise timekeeping device.”
Atomic clocks operate by monitoring the resonant frequency of atoms, whereas quantum clocks measure very slight changes in these atoms’ energy levels (‘quantum fluctuations’), resulting in greater accuracy even compared to super-accurate atomic clocks.
‘Atomic clocks are already very precise. In fact, a quantum clock has the potential to retain its accuracy, only losing a single second after an extremely long period of nearly three billion years.’
The British quantum clock project will be the first of its kind to be created in the UK, according to a statement from the UK government; however, it will not be the first of its kind in the world.
In 2010, researchers at the University of Colorado at Boulder collaborated with the US National Institute of Standards and Technology to create a quantum clock.
However, key barriers to deploying quantum clocks are their size – current models come in a van or in a car trailer and occupy around 1,500 litres in volume.
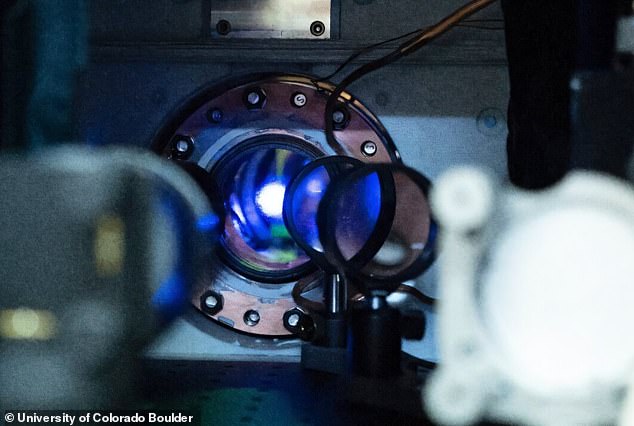


Similar to most quantum devices, quantum systems also exhibit sensitivity to environmental factors such as temperature and air molecules, which constrains their transportation between various locations.
“Quantum clocks are not tiny, like wristwatches or alarm clocks,” France stated.
These are devices that in current implementations are often quite large, capable of occupying an entire room.
With advancements in technology, these devices will shrink in size, becoming more portable and convenient to carry.
Beyond just its ultra-precise timekeeping, quantum clocks has the potential to transform global navigation systems, providing significant advancements in satellite communications and aircraft navigation.
A new quantum clock developed by DSTL will enable the creation of more precise and independent navigation systems, reducing reliance on GPS satellites that can be vulnerable to interference or destruction in conflict situations.
This technology will augment communication systems, including heavily encrypted military networks, which require extremely precise timing, as well as enhance the precision of sophisticated weapon systems such as guided missiles, which need exact timing to determine trajectories and coordinate strikes.
Moreover, the British Armed Forces will gain an advantage over their adversaries in “timing-critical operations”, such as cyber warfare, where even small delays can be decisive.
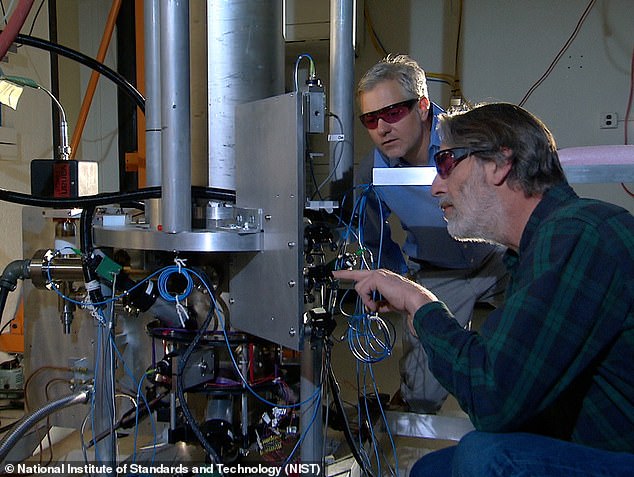

Electronic warfare refers to the actions by a country or international organization to attack and attempt to damage another country’s computers or information networks.
France stated, ‘Precise timekeeping is crucial for governments and armed forces, allowing for accurate navigation via GPS technologies or similar systems, as well as the guidance of weapon systems like missiles.
‘The security of communications is equally vital for both the military and civilians.’
The majority of secure communications for governments and the military relies on precise timing sources to operate effectively.
‘But these accurate clocks also have numerous uses in civilian applications and general internet security, even protecting your personal data as it’s transmitted over the internet.’
Corporations and governments globally are eager to capitalize on the vast potential advantages that the unusual effects of quantum technology could provide.
Google recently introduced a novel quantum computing processor, which can allegedly achieve a specific task much faster than today’s leading supercomputers, requiring 10 septillion years to accomplish the same task, a timeframe that is equivalent to several billion years after the estimated age of the universe.
Ultimately, such a chip could power a “commercial” quantum computer that can be bought by the general public and utilized in laboratories, offices, and even residences.
and discover lifesaving drugs.
Read more










